The performance and stability of chemicals are crucial to their application. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), as a thermal analysis technique, can provide information on heat flow changes during heating or cooling of a substance, thereby helping researchers understand the thermal properties of the substance, such as melting point, crystallinity, glass transition temperature, thermal stability, etc. This information is of great significance for the synthesis, processing and application of materials.
Differential Scanning Calorimeters work by measuring the energy difference caused by the temperature change of a sample and a reference during heating or cooling. When a sample undergoes physical or chemical changes, it absorbs or releases heat, resulting in a temperature difference between the sample and the reference. The differential scanning calorimeter system records this temperature difference and converts it into a heat flow signal, thereby obtaining the thermal properties of the sample.
1. Test Method
- Test equipment
Instrument model: DSC3000 differential scanning calorimeter
Instrument brand: Xiangyi Instruments Xiangtan Limited

- Sample preparation
Before DSC testing, you need to prepare an appropriate amount of resin sample. The sample should be uniform, dry, and avoid contact with moisture or other contaminants in the air.
- Test steps
3.1. Place the sample and reference in the sample chamber and reference chamber of the DSC instrument respectively.
3.2. Set the test temperature range from room temperature to 200°C and the heating rate to 10°C/min.
3.3. Start the test and the DSC system automatically records the heat flow difference between the sample and the reference.
3.4. Analyze the DSC curve to obtain the required thermal property information.
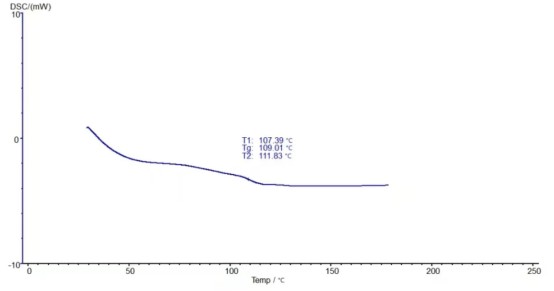
The glass transition temperature of this resin is 109 degrees Celsius
Application of Differential Scanning Calorimeter in Chemical Product Testing
- Thermal stability test
Thermal stability is one of the important performance indicators of chemical products. Through DSC testing, it is possible to determine whether a substance undergoes decomposition, oxidation or other chemical reactions during heating, as well as the starting temperature and thermal effects of these reactions. This is crucial for evaluating the application performance and safety of materials at high temperatures.
- Phase change and melting point determination
DSC can be used to determine phase change characteristics such as melting point, crystallinity and glass transition temperature of a material. This information is important for understanding the physical state and processing properties of the material. For example, the glass transition temperature of a polymer material can affect its mechanical properties and processing conditions.
Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) is a powerful thermal analysis tool that is widely used in chemical product testing. Through DSC testing, the thermal properties, thermal stability, phase change characteristics and reaction kinetics of substances can be obtained, providing important theoretical and practical guidance for the synthesis, processing and application of materials.
