As an important thermal analysis technique, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is widely used in the study of thermal stability of materials. This paper studies the thermal decomposition behavior of plastic particles through thermogravimetric analysis technology, explores the thermal decomposition temperature and weight loss corresponding temperature of plastic particles, and provides a theoretical basis for the processing and application of plastic particles.
1. Introduction
Plastic particles are an indispensable basic material in modern industry, and their thermal stability directly affects the material processing technology and product performance. Thermogravimetric analysis technology can accurately measure the mass change of materials during heating, thereby determining the thermal decomposition temperature and weight loss corresponding temperature of the material, which is of great significance for evaluating and improving the thermal stability of plastic particles.
2. Experimental part
2.1 Materials and Instruments
Plastic particle samples: standard plastic particles.
Instrument: TGA1001 thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA).

2.2 Experimental methods
2.2.1. Instrument: TGA1001 Thermogravimetric Analyzer (TGA) Aluminum crucible tweezers
2.2.2 Gas: Nitrogen
2.2.3 Sample: Plastic particles
2.2.4. Main experimental parameters: Sample weight: 20±3mg Gas flow rate: 50±10ml Heating rate: 10°C/min Cut-off temperature: 300°C
Weigh the plastic particle sample accurately and place it in the crucible of TGA. Set the heating program, including the heating rate, atmosphere (such as nitrogen or air), etc. Start the experiment as shown below and record the mass change of the sample as the temperature rises.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1 Thermogravimetric curve analysis
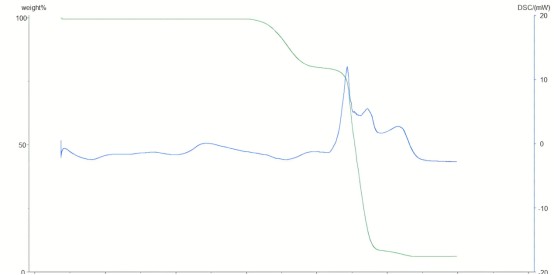
Through TGA experiments, we obtained the thermogravimetric curve (TG curve) and differential thermogravimetric curve (DTG curve) of plastic particles. The TG curve shows the mass loss of plastic particles during heating, while the DTG curve reflects the rate of mass loss.
3.2 Determination of thermal decomposition temperature
According to the TG curve, we can determine the initial decomposition temperature (Ti), the temperature corresponding to the maximum weight loss rate (Tmax) and the final decomposition temperature (Tf) of the plastic particles. These temperature points are key parameters for evaluating the thermal stability of plastic particles.
3.3 Analysis of temperature corresponding to weight loss
Through analysis, we can identify the weight loss behavior of plastic particles at different temperatures. The weight loss temperature refers to the temperature at which the mass loss of the plastic particles reaches a certain percentage at a specific temperature.
3.4 Discussion of influencing factors
The effects of heating rate, atmosphere, sample amount and particle size on TGA results were considered in the experiment. By optimizing the experimental conditions, we were able to obtain more accurate thermal decomposition temperature and weight loss corresponding temperature.
4. Conclusion
Thermogravimetric analysis technology provides an effective method for studying the thermal stability of plastic particles. By measuring the thermal decomposition temperature and weight loss corresponding temperature of plastic particles, we can better understand the thermal behavior of materials and provide a scientific basis for the processing and application of plastic particles.
