Thermogravimetric analysis is a technique for analyzing the composition and thermal stability of a sample by measuring the change in mass of the sample during heating under a controlled atmosphere. This article introduces in detail the method of testing carbon black content and ash content using thermogravimetric analysis, including experimental principles, operating steps, influencing factors and result analysis.
- Introduction
Carbon black is an important additive in rubber and plastic products. Its content and properties directly affect the quality and performance of the products. Ash content is an inorganic impurity in carbon black, and its content also needs to be strictly controlled. Traditional testing methods have problems such as cumbersome steps and long time consumption. Thermogravimetric analysis has the advantages of simple operation and accurate results, and has gradually become an important means of testing carbon black content and ash content.
- Experimental Principle
Thermogravimetric analysis is based on the change in mass of a sample during heating. Carbon black loses volatile components during heating, while ash remains at high temperatures. By analyzing the thermogravimetric curve, the thermal stability and content of carbon black, as well as the ash content of the sample, can be determined.
- Operation steps
3.1 Sample preparation
Accurately weigh a certain amount of carbon black sample and spread the sample evenly in the crucible of the thermogravimetric analyzer.
3.2 Measuring instruments
TGA1001 Thermogravimetric Analyzer

3.3 Equipment parameter setting
Under a nitrogen atmosphere, the temperature was raised from room temperature to 600 degrees Celsius at a rate of 20 degrees Celsius/min and kept constant for 15 minutes to allow the sample to be fully pyrolyzed; after being kept constant at 600 degrees Celsius, the oxygen atmosphere was switched and the temperature was raised to 900 degrees Celsius at a rate of 20 degrees Celsius/min to allow the carbon black to be fully oxidized.
3.4 Testing Process
Start the thermogravimetric analyzer and record the mass change of the sample.
- Results Analysis
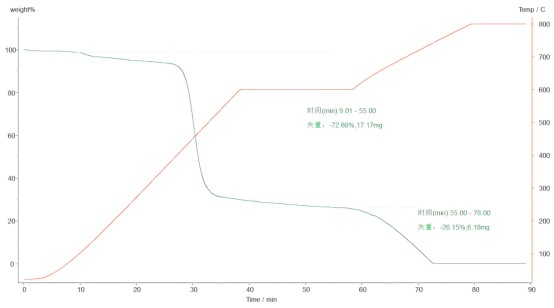
Figure 1
4.1 Carbon black content (%)
The thermal weight loss rate of carbon black is calculated by the weight loss point of the thermogravimetric curve in Figure 1, and the carbon black content is calculated based on the thermal weight loss rate.
After being kept at 600℃, the sample lost 17.17mg of weight. After being heated to 800℃, the sample lost 6.18mg of weight. The total mass of the sample is 23.6mg. The carbon black content is 26.1% according to the formula (carbon black content calculation formula: (m2-m3)/m1 x 100%)
4.2 Ash content (%)
At high temperatures, after carbon black is completely oxidized, the remaining mass is ash.
Calculate the ash content based on the mass of the ash. The ash content is 1.05%. (Ash content calculation formula: (m2-m0)×100/(m1-m0))
- Conclusion
Thermogravimetric analysis is a fast and accurate method for testing carbon black content and ash content. By optimizing the test conditions and analysis methods, reliable test results can be obtained, providing an important basis for carbon black quality control and product development.
- Test reference standards
GB/T 13021-1991 Determination of carbon black content of polyethylene pipes and fittings (thermal gravimetric method)
DB35/T 1558-2016 Determination of carbon black content in polyolefin products by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
